Distributed consensus optimization (DCO) is a common problem definition for optimization problems in networked systems. In DCO, there is a local objective function for each node, and the systematic objective function, i.e. global objective function, is the sum of all local objective functions. DCO aims to minimize the global objective function and make the nodes reach a consensus on the final solution. There are two major features of DCO, limited local information and no-center local communication. First, each node can only access its own local objective function. This is because the local objective function is usually related to the privacy data, real-time data, or mass data stored in terminal devices, which cannot be transmitted to other nodes. What’s more, the local objective functions of different nodes are usually conflicting to some extent. Second, the communication network of DCO is usually a not-fully-connected graph without a center node. Nodes can only communicate with immediate neighbors in the graph. This feature increases the difficulty of fast information transfer among nodes. In the literature, lots of first-order algorithms have been proposed based on consensus theory and gradient descent method. However, black-box and non-convex DCO still remains promising and challenging.
The goal of the competition is to encourage participants to use zero-order optimization algorithms such as evolutionary computation to improve performance of black-box and non-convex DCO. To this end, we design a set of benchmark functions for black-box distributed consensus optimization. This benchmark set considers different communication environments, conflict degrees, node homogeneity, and types of objective functions. The main rule of this competition is to find the best possible global solution under the specified number of evaluations, while taking into account the consensus of the system and the communication efficiency.
Submission deadline: June 10, 2024
Notification (final ranking): June 28, 2024
You can submit your related code and results via emails to [email protected].
Offical website: Competition-on-Black-box-Consensus-based-Distributed-Optimization
Each team can write and submit a paper via the conference system that describes the method and the results obtained for solving the task given by the competition, but this is not mandatory. The submitted papers will be reviewed as any other papers submitted to WCCI2024. During the conference, the participants demonstrate their solutions, which are evaluated by a jury. After demonstrations conclude, the jury announces the winner of the competition. Moreover, those teams who submitted papers will present accepted papers at the conference (e.g., during a special session).
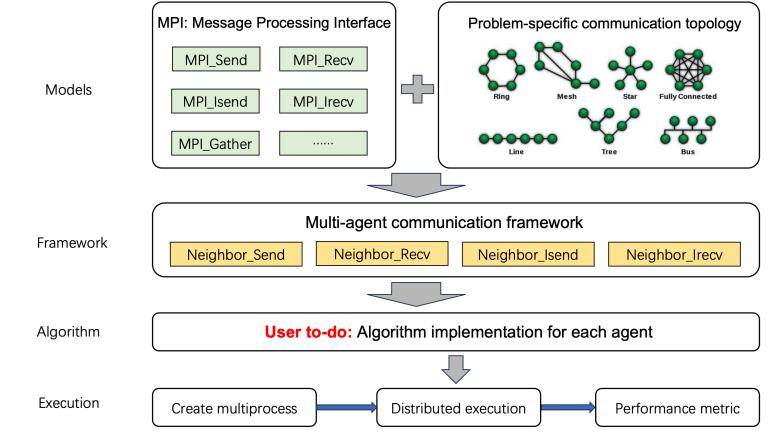
The competition provides an algorithm development platform for CDO. This platform provides interfaces for evaluation functions, communication, and performance evaluation, allowing developers to focus only on algorithm design. First, we design 5 groups of 36 benchmark functions in total for black-box CDO, and provide evaluation interfaces for these functions. Second, we provide peer-to-peer communication interfaces based on the communication topology of benchmark functions. These interfaces Confirm that each node can only communicate with immediate neighbors. Third, we provide the performance evaluation interface for algorithms, including solution quality, communication efficiency, and system consensus. The code is available in
Wei-Neng Chen (Senior Member, IEEE) South China University of Technology, China. Email: [email protected]
Wei-Neng Chen received the bachelor’s and Ph.D. degrees in computer science from Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China, in 2006 and 2012, respectively. Since 2016, he has been a Full Professor with the School of Computer Science and Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou. He has coauthored over 100 international journal and conference papers, including more than 70 papers published in the IEEE TRANSACTIONS journals. His current research interests include computational intelligence, swarm intelligence, network science, and their applications. Dr. Chen was a recipient of the IEEE Computational Intelligence Society Outstanding Dissertation Award in 2016 and the National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars in 2016. He was also a PI of the National Science and Technology Innovation 2030—the Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Key Project. He is currently the Vice-Chair of the IEEE Guangzhou Section, and the Chair of IEEE SMC Society Guangzhou Chapter. He is also a Committee Member of the IEEE CIS Emerging Topics Task Force. He serves as an Associate Editor for the IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NEURAL NETWORKS AND LEARNING SYSTEMS and the Complex and Intelligent Systems.
Tai-You Chen (Student Member, IEEE) South China University of Technology, China. Email: [email protected]
Tai-You Chen received the bachelor’s degree in computer science and technology from the South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, in 2022, where he is currently pursuing the Ph.D. degree in computer science and technology with the School of Computer Science and Engineering. His current research interests include swarm intelligence, evolutionary computation, consensus-based distributed optimization, multi-agent systems, and their applications in real-world problems.
Feng-Feng Wei (Student Member, IEEE) South China University of Technology, China. Email: [email protected]
Feng-Feng Wei (S’23) received the bachelor’s and Ph.D. degrees in computer science and technology from the South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, in 2019 and 2023, respectively. She is currently a research assistant with the Guangdong-Hong Kong Joint Innovative Platform of Big Data and Computational Intelligence, South China University of Technology.
Her current research interests include swarm intelligence, evolutionary computation, distributed optimization, edge–cloud computing, and their applications on data-driven optimization in real-world problems.


